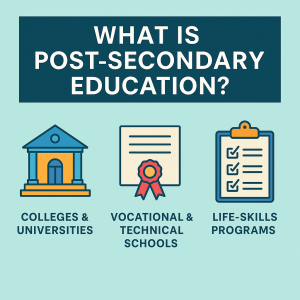
What Is Post Secondary Education ?
Hello everyone, I’m Richard, an observer and writer who has been deeply involved in the education sector for many years. Recently, I’ve noticed an interesting trend: many people are searching for “what is post secondary education,” yet they never seem to find a truly satisfying answer. They click, they browse, and then they leave, often with more questions than they started with.
Why This Question Matters Now More Than Ever
Today, I want to talk with you about this crucial concept—one that shapes countless futures—in a more direct and accessible way. Let’s set aside the stiff, formal definitions and explore what it truly means.
Breaking the Myth: Post Secondary Education ≠ University
First, let’s dismantle the most common misconception: when people hear “post secondary education,” the image that often comes to mind is a traditional four-year university. While that’s part of the picture, it’s far from the whole story.
Simply put, post secondary education refers to any formalized learning you pursue after completing high school (or its equivalent, like a GED).
Yes, it’s that straightforward. The core idea is “after high school,” and its scope is incredibly broad. Think of it as a large “family” of educational options. A university is just one of its most well-known members, and it’s helpful to understand the difference between the terms. According to the U.S. Department of State’s EducationUSA network, a university typically offers both undergraduate and graduate degrees, while colleges often focus on undergraduate programs. You can read more in their FAQ on the U.S. educational system.
So, Who Else Is in This “Family”?
Broaden your perspective, and you’ll discover a world of opportunity. Besides the familiar Universities, post-secondary education also includes Community Colleges, Vocational Schools, and various Certificate programs.
To make the differences clearer, here’s a simple comparison table:
As you can see from the table, the true post secondary education meaning is about choice. It provides a diverse set of runways. For example, many students start at a community college and then take advantage of university transfer programs to complete their bachelor’s degree. Others may find that a technical school leads directly to high-paying jobs that don’t require a bachelor’s degree, as documented by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Why Is Understanding the True Meaning of Post-Secondary Education So Important?
Because it directly impacts your future—and your children’s future.
When we are no longer limited by the “university-or-bust” mindset, we can make wiser, more personalized decisions. A young person passionate about coding might thrive in an intensive tech boot camp. A student aiming to enter the healthcare field quickly might find their ideal starting point in a community college’s nursing program.
Ultimately, success in any of these paths doesn’t just depend on the choice of institution, but also on how effectively you learn. Mastering effective study skills is the universal key that unlocks potential, regardless of the educational environment.
The “best” education isn’t the most expensive or the most prestigious; it’s the “most fitting.” Understanding the breadth of what is post secondary education empowers you to explore your options and choose a career path that truly fits you, a process the Federal Student Aid office provides excellent resources for.
Conclusion: Preparing for Your Next Step
So, the next time you see the term post secondary education, I hope you see not a vague concept, but a future filled with possibilities. It’s more than just a diploma; it’s a strategic investment you make in yourself to achieve your personal and professional goals.
I hope this guide has helped clear the fog. The world of education is vast, and this is just the beginning of the conversation. If you’re ready to explore further, you can discover more expert guides and resources on www.newlookeducation.com to continue planning your unique journey.